How to Service Entrence Cable on the Back of a Box
 Electrical Service Entry Cable Sizes for Long Wire Runs
Electrical Service Entry Cable Sizes for Long Wire Runs
How much to increase SEC wire size over longer distances
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about electrical wire sizes, diameters, and ampacity ratings
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
Electrical service entry wire sizes are calculated for long wire runs in which the wire size must be increased to avoid an un-wanted voltage drop. We include links to wire size and voltage drop calculators.
This article series gives photos and tables of electrical service entry cable sizes, electrical branch circuit wire sizes, bell wire, telephone wire, thermostat wire, and ampacity or fuse/circuit breaker ratings.
We also provide an ARTICLE INDEX for this topic, or you can try the page top or bottom SEARCH BOX as a quick way to find information you need.
Tables of SEC Sizes for Long Wire Runs for Copper & Aluminum Cable
This page gives the necessary increase in electrical service entry wire size for long runs, for example between the electric meter and the main electrical panel.
If you need wire sizes for shorter service entry cables up to 200A or for both short and long branch circuit wires from 15 to 50A
see SE CABLE & BRANCH CIRCUIT WIRE SIZES vs AMPS
Summary Table of Service Entry Cable Sizes
(Detailed tables follow the table given just below)
Electrical Service Entry Wire Sizes Needed for Longer Run Lengths | ||||||||
Maximum Run Length in Ft. vs AWG Wire Size, @ <= 3% Voltage Drop, 120V per SEC Conductor | ||||||||
| 25 ft. | 50 ft. | 100 ft. | 150 ft. | 200 ft. | 300 ft. | 400 ft. | ||
| Wire Material | AMPS | Wire Size AWG | ||||||
| Copper | 100A | 4 | 4 | 1 | 2/0 | 3/0 | 300 kcmil | 500 kcmil |
| Aluminum | 100A | 2 | 2 | 2/0 | 4/0 | 300 kcmil | 600 kcmil | 1000 kcmil |
| Copper | 200A | 1/0 | 1/0 | 3/0 | 300 kcmil | 500 kcmil | 1000 kcmil | 500 kcmil3 |
| Aluminum | 200A | 2/0 | 2/0 | 300 kcmil | 600 kcmil | 1000 kcmil | 600 kcmil 3 | 1000 kcmil3 |
Notes to the table above
- Using two 120VAC conductors, <= 3% maximum drop in voltage
- 240V Service provided as two separate 120VAC cables; All of these services are single phase. Three phase power typically reduces the wire size to the next smaller.
- Requires 2 parallel cable sets
- Watch out: these are example wire or cable sizes vs. run or length for the specific parameters named here and entered in the wire size and length calculator. Your installation may differ. For safety and for code compliant electrical wiring, be sure to check with your local electrical code inspector and electrical code provisions.
- Adapted from two sources:
- VOLTAGE DROP TABLE, [PDF], retrieved 2017/09/26, Cerrowire LLC, 1099 Thompson Road SE, Hartselle AL 35640, USA, Tel: 256-773-2522, original source: http://www.cerrowire.com/files/file/voltagedrop.pdf
The 300 ft and 400 ft cable length data is from
- Cable size recommended based on voltage drop calculations. Calculated by Online voltage drop calculator: 2019/07/23, Southwire, Tel: 1-800-444-1700 Website: www.southwire.com Email: CableTechSupport@southwire.com Web page: https://www.southwire.com/calculator-vdrop
Detailed Copper SEC Sizes for Longer Cable Distances
The table below shows Copper SEC wire sizes for various run lengths - be sure to see the additional assumptions in the table notes. The voltage drop is held to under 3% across the long distance wire runs in these tables.
Copper SEC Wire Size for Long Runs for 200A Service | |||
| Cable Size1 | Distance 8 Ft. / M | Voltage Drop % | Phase |
| 3/0 AWG | 200 - 2257 / 60 | 2.83 | 1 |
| 3/0 AWG | 200 / 60 | 2.45 | 3 |
| 4/0 AWG | 250 - 2607 / 75 | 2.89 | 1 |
| 4/0 AWG | 250 / 75 | 2.58 | 3 |
| 250 kcmil | 2907 / 88 | ||
| 250 kcmil | 2907 - 300 / 90 | 2.72 | 3 |
| 300 kcmil | 300 - 3207 / 90 | 2.78 | 1 |
| 300 kcmil | 350 / 100 | 2.82 | 3 |
| 350 kcmil | 3507/ 100 | 2.92 | 1 |
| 350 kcmil | 400 / 120 | 2.89 | 3 |
| 400 kcmil | 450 / 135 | 2.97 | 3 |
| 500 kcmil | 400 - 4307 / 120 | 2.67 | 1 |
| 600 kcmil | 450 - 4757 / 135 | 2.74 | 1 |
| 500 kcmil | 500 / 150 | 2.89 | 3 |
| 600 kcmil | 475 / 145 | 1 | |
| 750 kcmil | 500 - 5357 / 150 | 2.72 | 1 |
| 1000 kcmil | 6157 / 187 | 1 | |
Notes to the table above:
- Cable size recommended based on voltage drop calculations. Calculated by Online voltage drop calculator: 2019/07/23, Southwire, Tel: 1-800-444-1700 Website: www.southwire.com Email: CableTechSupport@southwire.com Web page: https://www.southwire.com/calculator-vdrop
- Electrical Panel & Service Size: 200A 240VAC, Ending amps if voltage drop were 3% will be 194A
- Voltage: 240 VAC
- Maximum Voltage Drop: 3%
- Parallels (Sets) 1
- Conductor installation is direct-buried, in conduit, OR overhead, unless otherwise noted
- See this ELECTRIC WIRE AMPACITY CHART [PDF] from CerroWire, retrieved 2021/11/25 original source: https://www.cerrowire.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/Cerrowire_Ampacity_Chart_210405.pdf
- Maximum wire run distance changes by required temperature rating:
The Amperage rating and distancees shown are for 90°C (194°F) THWN-2, THHN, XHHW-2, USE-2 - copper wire;
Watch out: Note that dropping to 60°C (140°F) NM-B, UF-B copper wire, the maximum run lengths will be substantially shorter.
- For smaller wire size ampacities & run lengths (#14 copper or #12 aluminum) up through typical residential SEC wire sizes and amps
See SE CABLE & BRANCH CIRCUIT WIRE SIZES vs AMPS
Watch out: the engineering work and derivation of the table above is derived from the sources listed below including manufacturer's tables and online voltage drop calculators but may not be correct for your specific installation. Check with your engineer or electrician.
Watch out: if you are not trained and qualified to install electrical wiring a mistake can result in fire, injury, or death. Be sure you review your work plan with your local electrical inspector and that work is done to the electrical code for the country and city where you live. In the U.S. that's the U.S. NEC.
Detailed Aluminum SEC Cable Sizes for Long Wire Runs
The table below shows Aluminum SEC wire sizes for various run lengths - be sure to see the additional assumptions in the table notes.
Aluminum SEC Wire Size for Long Runs for 200A Service | |||
| Cable Size1 | Distance Ft. / M | Voltage Drop % | Phase |
| 300 kcmil | 200 / 60 | 2.79 | 1 |
| 250 kcmil | 200 / 60 | 2.77 | 3 |
| 400 kcmil | 250 / 75 | 2.85 | 1 |
| 350 kcmil | 250 / 75 | 2.69 | 3 |
| 500 kcmil | 300 / 90 | 2.92 | 1 |
| 400 kcmil | 300 / 90 | 2.96 | 3 |
| 750 kcmil | 350 / 100 | 2.67 | 1 |
| 500 kcmil | 350 / 100 | 2.95 | 3 |
| 1000 kcmil | 400 / 120 | 2.61 | 1 |
| 750 kcmil | 400 / 120 | 2.64 | 3 |
| 1000 kcmil | 450 / 135 | 2.94 | 1 |
| 750 kcmil | 450 / 135 | 2.97 | 3 |
| Not Available | 500 / 150 | 1 | |
| 1000 kcmil | 500 / 150 | 2.83 | 3 |
Notes to the table above: Assumptions
- Cable size recommended based on voltage drop calculations. Calculated by Online voltage drop calculator: 2019/07/23, Southwire, Tel: 1-800-444-1700 Website: www.southwire.com Email: CableTechSupport@southwire.com Web page: https://www.southwire.com/calculator-vdrop
- Electrical Panel & Service Size: 200A 240VAC, Ending amps if voltage drop were 3% will be 194A
- Voltage: 240 VAC
- Maximum Voltage Drop: 3%
- Parallels (Sets) 1
- Conductor installation is direct-buried, in conduit, OR overhead, unless otherwise noted
Watch out: if you are not trained and qualified to install electrical wiring a mistake can result in fire, injury, or death. Be sure you review your work plan with your local electrical inspector and that work is done to the electrical code for the country and city where you live. In the U.S. that's the U.S. NEC.
How to Use a Voltage Drop Calculator to Determine Reqired Service Entry Wire Size
Here we give examples and compare the results of using two example wire size and voltage drop calculators.
You will see that Southwire and Paige calculators give similar results.
1. Southwire's Voltage Drop Calculator example calculating SEC wire size
Southwire's wire size calculator at http://www.southwire.com/support/voltage-drop-calculator.htm is easy to use and clear.
The user specifies the number of phases (1 or 3), conductor (copper or aluminum), installation (direct buried, conduit, or overhead) and the input voltage, maximum allowed voltage drop (I use 3%), the length of the cable run, and the desired current (amps) at the end of the cable run. The calculator gives an appropriate wire selection and its parameters, such as this:
Example: Single phase, aluminum conductor, direct buried, 120VAC, 3% maximum voltage drop, 250 ft. cable run length, 100A current at end of cable
Result: 1 conductors per phase utilizing a #400 Aluminum conductor will limit the voltage drop to 2.94% or less when supplying 100.0 amps for 250 feet on a 120 volt system.
Changing the example above to 240 VAC, keeping other parameters the same gives this result:
Result: 1 conductors per phase utilizing a #3/0 Aluminum conductor will limit the voltage drop to 2.82% or less when supplying 100.0 amps for 250 feet on a 240 volt system.
2. Paige Wire Size Calculator example calculating SEC wire size
Paige Wire's voltage wire size calcuator at http://www.paigewire.com/pumpWireCalc.aspx is also easy to use and clear. Testing with the following parameters:
Example: 240 VAC Single Phase, 100A, 250 ft. run, 3% voltage drop allowed,
Result: 1 AWG Copper or 2/0 Aluminum
Changing the example above to 120VAC, keeping other parameters the same gives this result:
Result: 3/0 AWG Copper or 250 MCM Aluminum
Siemens offers an XLS spreadsheet [ http://w3.usa.siemens.com/us/internet-dms/internet/consultingengineerscomm/general/Docs/DA_VD_Calculator_V1.1.xls - this address leaves InspectApedia.com] that can be used to calculate voltage dropas do other sources, and there are numerous online voltage drop calculators - I like the Southwire calculator given above. Be sure to compare the calculator's result with what the applicable electrical code will permit.
Voltage Drop Index - VDI - when to increase wire size for long electrical wire runs
The voltage drop index or VDI is a reference number that is based on the electrical resistance of a wire and is calculated as
VDI = (Amps x Feet of run) / (% Voltage Drop allowed x Voltage)
Typical allowable voltage drop is 2% or 4% depending on the application.
3% is the most commonly-accepted voltage drop target.
More about the VDI and VDI tables are given
at SE CABLE & WIRE SIZE TABLES vs AMPS
Question: what size Aluminum Service Entry Cable do I need for a 200A panel on a 400 foot length?
2019/07/23 Bob s. said:
I'm running a 400 foot main cable from street to home, I want 200amp service and use aluminum wire. What size do I use to compensate for distance
Reply:
From the table of Aluminm SEC Cable Sizes for Long Runs you'll see the answers given below,
Answer: 200A, Aluminum wire, 400 foot run, direct buried SEC cable
For single phase power: 1000 kcmil aluminum wire will have a voltage drop under 3% fora 400 foot run of direct buried cable and a 200VAC single phase electrical service. That gives us 194 Amps at the end of the SEC run.
For three phase power: 750 kcmil aluminum wire will have a voltage drop under 3% for a 400 foot run of direct buried cable and a 200VAC three phase electrical service. That gives us 194 Amps at the end of the SEC run.
Using a typical online voltage drop calculator, keeping your voltage drop belwo 3%, and using your 400 foot run and Aluminum wire for a 200 VAC service, we plugged the data into Southwire's voltage drop calculator to see what wire size would suit.
Details about Wire Size vs Voltage Drop for Long SEC Wire Runs
Voltage drop across a wire is proportional to the current flow and wire resistance; for AC power such as your service entry cable (SEC) total impedance and power factor (the ratio of power loss) are considered too.
None of the standard voltage drop tables go beyond 200 feet of wire run. At 200 ft and 200A the tables get to 350 to 500MCM copper wire and for 200 ft and 200A the tables get to 600 MCM aluminum wire (Cerrowire.com)
For longer runs (like your 400 ft) your engineer would either perform the voltage drop calculation and wire size. Or use one of the online voltage drop calculators. Southwire provides an easy-to-use voltage drop calculator that I recommend. .
I expect you're going to end up with at least 600 or 750 MCM AL wire - such a large size may not be practical even though the Cu will of course be more expensive. Let's look at the details.
- Example calculation 1 - Copper Wire, 1 phase power
- Power Factor: 100%
- Wire Size: 500 kcmil Copper
- Phase: Single phase
- Conductor: Aluminum
- Installation: Direct buried
- Voltage: 240VAC
- Cable run: 400 ft.
- Maximum voltage drop: 3%
- Current at end of cable: 194 Amps (200A - [.03 x 200])
- Calculated Voltage Drop: with 500 kcmil copper wire: 2.67% - this is within the 3% limit
1 conductor per phase utilizing a 500 kcmil Copper conductor installed Direct Buried will limit the voltage drop to 2.67% or less when supplying 194 amps for 400.0 feet on a 240 volt 1 phase system.
- Example calcuation 2 - Aluminum Wire, 1 phase power
- Power Factor: 100%
- Wire Size: 1000 kcmil Aluminum
- Phase: Single phase
- Conductor: Aluminum
- Installation: Direct buried
- Voltage: 240VAC
- Cable run: 400 ft.
- Maximum voltage drop: 3%
- Current at end of cable: 194 Amps (200A - [.03 x 200])
- Calculated Voltage Drop: 1000 kcmil aluminum wire: 2.61% - this is within the 3% limit
1 conductor per phase utilizing a 1000 kcmil Aluminum conductor installed Direct Buried will limit the voltage drop to 2.61% or less when supplying 194 amps for 400.0 feet on a 240 volt 1 phase system.
- Example calcuation 2 - Aluminum Wire, 3 Phase power
- Power Factor: 100%
- Wire Size: 750 kcmil Aluminum
- Phase: Three phase
- Conductor: Aluminum
- Installation: Direct buried
- Voltage: 240VAC
- Cable run: 400 ft.
- Maximum voltage drop: 3%
- Current at end of cable: 194 Amps (200A - [.03 x 200])
- Calculated Voltage Drop: 1000 kcmil aluminum wire: 2.64% - this is within the 3% limit
1 conductor per phase utilizing a 750 kcmil Aluminum conductor installed Direct Buried will limit the voltage drop to 2.64% or less when supplying 194 amps for 400.0 feet on a 240 volt 3 phase system.
- Example calcuation 2 - Copper Wire, 3 Phase power
- Power Factor: 100%
- Wire Size: 750 kcmil Aluminum
- Phase: Three phase
- Conductor: Aluminum
- Installation: Direct buried
- Voltage: 240VAC
- Cable run: 400 ft.
- Maximum voltage drop: 3%
- Current at end of cable: 194 Amps (200A - [.03 x 200])
- Calculated Voltage Drop: 350 kcmil copper wire: 2.89% - this is within the 3% limit
1 conductor per phase utilizing a 750 kcmil Aluminum conductor installed Direct Buried will limit the voltage drop to 2.64% or less when supplying 194 amps for 400.0 feet on a 240 volt 3 phase system.
Online voltage drop calculator used: 2019/07/23, Southwire, Tel: 1-800-444-1700 Website: www.southwire.com Email: CableTechSupport@southwire.com Web page: https://www.southwire.com/calculator-vdrop
Key points in calculating voltage drop and selecting wiring cable
- 3% is the typical allowable voltage drop for SEC feeder wires
- 5% is the maximum recommended voltage drop for individual branch circuits.
- The 200A service is not necessarily the amps used in the voltage drop calculation though we've kept the 200A figure for these example calculations. The engineer doing a direct voltage drop calculation adds up the anticipated current load or wattages for all of the circuits being fed from the panel.
Total Watts / Circuit Voltage (110 or 220) = Total AMPS [Or more conservative: use your nominal 200A panel and breaker rating]
- Watch out: with a 400 foot run your 200A wire size may be so big that it will not fit in the standard wiring lugs in your 200A panel. Your electrical supplier an provide a wire size reducer that can make the connection between a larger diameter SEC wire and the lugs in your electrical panel.
- Watch out : when running larger service wires you may also need to run a larger service panel grounding conductor to earth.
Reader Comments & Q&A
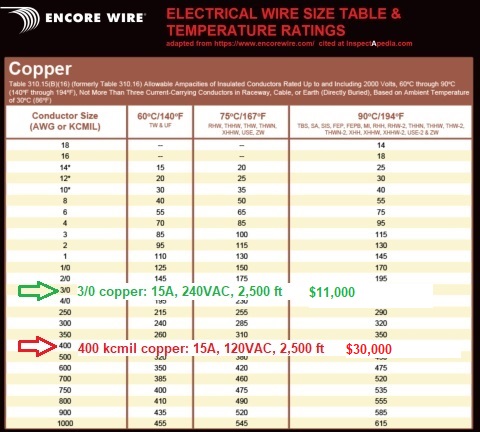 Really? you ran or plan to run #10 copper wire 2,500 feet - nearly half a mile of electrical wire. In conduit?
Really? you ran or plan to run #10 copper wire 2,500 feet - nearly half a mile of electrical wire. In conduit?
There is simply no way that you can run a conventional 15A o 20A 120V or even 240V wire using #10/2 copper wire from your home to a barn that's nearly half a mile away using any conventional wiring means. The wire will have such a large voltage drop that your delivery voltage will be too low and your pump either won't run or will have constant trouble.
Here we discuss using a voltage drop calculator (we like one provided by Southwire) at which you input the basic parameters of
- cable run length
- voltage
- allowable voltage drop (usually limited to 3%)
- current(amp) required at end of cable
- number of parallel wire set
I ran your case for two solutions:
Case 1: 2500 ft., 15Amps, 120VAC, and the wire size calculator returns
1 conductor per phase utilizing a 400 kcmil Copper conductor installed Direct Buried will limit the voltage drop to 2.95% or less when supplying 15 amps for 2500.0 feet on a 120 volt 1 phase system.
OR
Case 2: 2500 ft., 15Amps, 240VAC, and the wire size calculator returns
1 conductor per phase utilizing a 3/0 AWG Copper conductor installed Direct Buried will limit the voltage drop to 2.74% or less when supplying 15 amps for 2500.0 feet on a 240 volt 1 phase system.
Frankly, if I were going to the trouble and cost of running half a mile of electrical wire I'd run a 240V line to have a bit more capacity at the other end -
and I'd consider going to a 20A circuit, for which you'd need
1 conductor per phase utilizing a 250 kcmil Copper conductor installed Direct Buried will limit the voltage drop to 2.69% or less when supplying 20 amps for 2500.0 feet on a 240 volt 1 phase system.
Why? What are the chances that once electrical service is brought to an isolated building nobody is going to want to run more than just a well pump? What about a light, or a receptacle to power an electric drill?
Shown above is a wire size table adapted from Encorewire.com cited theron
I'd do some shopping or consider an alternative power source (Solar ?)
Consider that at some suppliers we checked online (you may find better price from a bulk electrical wire supplier)
the price for 2,500 ft of 3/0 copper electrical wire is over $11,000. U.S.
the price for 2,500 ft. of 400 kcmil copper wire is around $30,000 U.S.
Thats for using UF-rated wire - intended for direct burial into soil.
If you instead want to try to run half-a mile of conduit - not something that's necessary in my OPINION, and if you used a 3/4" diameter flexible water-tight non-metal conduit like that provided by Southwire, shown below, you may save by buying individual conductors instead of sheathed UF SEC cable, at $136 / 100 ft., you'll add about another $3,400. U.S. varying up or down in cost depending on the conduit diameter needed.

This flexible conduit is rated as permittd for direct burial or for burial in concrete. The conduit wall is Schedule-40.
Also see conduit products from Hydromaxx.
I have 10/2 UF-B Wire w/ Ground which runs underground with no conduit for 2500 feet from the control box in the barn to the two pressure tanks in my pump house.
This is the third time it is shorting out and the well person who installed the system saids he is not an electrician and unable to recommend what kind of wire I need to replace it with.
Something about it is bleeding over causing the short.
Sending 120 volts up the wire and only receiving 58 volts back = which is burning the control components up.
What would be the correct kind and size of the wires to tell the pump to turn off.
There is hardly any load on the wires what would I replace it with?
Any feedback would be greatly appreciated. 503-663-2244 priano@gmail.com
@Jerry,
When you get to longer lengths than illustrated above on this page, you need to go to an online voltage drop calculator as noted above, such as:
http://www.southwire.com/support/voltage-drop-calculator.htm
or
http://www.paigewire.com/pumpWireCalc.aspx
The section above:
How to Use a Voltage Drop Calculator to Determine Required Service Entry Wire Size
will help you in using those online calculators.
Using a voltage drop calculator as we suggested, you'll see that if you allow a 3% voltage drop your copper wire size for a 15A circuit at 120V and 650 ft needs to be a #2 AWG copper wire
3% is the recommended allowable voltage drop
5% is the maximum permitted drop on a typical branch circuit;
If you accept 5% voltage drop your copper wire could be #4 AWG.
For other readers:
For branch circuits at 15A up to 50A and for distances up to 400 ft
you will find our
Branch Circuit Wire Sizes Needed for Longer Run Lengths Table
at SE CABLE & WIRE SIZES vs AMPS
What size/type direct burial cable do I need to provide 15 amps with at the end of a 650 ft run?
@Anonymous,
Please take a look in the table "Copper SEC Wire Size for Long Runs for 200A Service" at the top of this page.
what size wire for 200amp 140 foot run underground
@Larry, please check the sizing tables in the article above and let me know if any of that is unclear or confusing
What size service entrance cable do I need for a 100 amp service and a 150 ft. run?
Tim
Check out
SE CABLE SIZES FOR LONG WIRE RUNS
at https://inspectapedia.com/electric/Long-Run-SEC-Cable-Sizes.php
and don't hesitate to ask if that leaves you with questions
Thanks This Q&A were posted originally at UNDERGROUND SERVICE LATERAL FAQs
I'm putting underground electric service to my house. I have 200 amp service. I need 200 feet of underground. What size wire do I need.
Bob,
Please check out the table for long runs of aluminum service entry cabling at SE CABLE & WIRE SIZES FOR LONG RUNS
at https://inspectapedia.com/electric/Long-Run-SEC-Cable-Sizes.php
where I repeat your question and give a detailed reply.
Let me know if that information is not clear or if you're left with questions.
I'm running a 400 foot main cable from street to home, I want 200amp service and use aluminum wire. What size do I use to compensate for distance
...
Continue reading at SE CABLE & BRANCH CIRCUIT WIRE SIZES vs AMPS - topic home, or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Articles on Determination of Ampacity & Voltage at Building Electrical Services
- AMPS VOLTS DETERMINATION - home
- AMPS, LIMITING FACTORS
- AMPS & SEC SIZES
- AMPS & VOLTS, DETERMINE VISUALLY
- AMPS MEASUREMENT AUTOMOTIVE DC
- AMPS MEASUREMENT METHODS
- AMPACITY, MAIN DISCONNECT
- DEFINITIONS AMPS VOLTS WATTS
- ELECTRIC METERS & METER BASES
- ELECTRIC MOTOR HORSEPOWER & CIRCUIT WIRE SIZE
- ELECTRICAL PANEL AMPACITY
- VOLTAGE at the SEC
- UNDERGROUND SERVICE LATERALS - buried Service Entry Cables
- GROUND SYSTEM INSPECTION - home
- SAFETY for ELECTRICAL INSPECTORS - home
- SE CABLE & BRANCH CIRCUIT WIRE SIZES vs AMPS
- SE CABLE & WIRE SIZES FOR LONG RUNS
- SERVICE ENTRY WIRING & AMPACITY - wire sizes
- SIZE of WIRE REQUIRED for ELECTRICAL RECEPTACLES for receptacle circuits and similar wiring situations
- VOLTS / AMPS MEASUREMENT EQUIP
Suggested citation for this web page
SE CABLE & WIRE SIZES FOR LONG RUNS at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to ELECTRICAL INSPECTION & TESTING
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
...
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Questions & answers or comments about electrical wire sizes, diameters, and ampacity ratings.
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Technical Reviewers & References
Click to Show or Hide Citations & References
Publisher InspectApedia.com - Daniel Friedman
How to Service Entrence Cable on the Back of a Box
Source: https://inspectapedia.com/electric/Long-Run-SEC-Cable-Sizes.php
0 Response to "How to Service Entrence Cable on the Back of a Box"
Post a Comment